UbiQTree: Uncertainty quantification in XAI with tree ensembles
Dubey, A., Anžel, A., İlgen, B., & Hattab, G. (02 2026). UbiQTree: Uncertainty quantification in XAI with tree ensembles. Patterns (New York, N.Y.), (101454), 101454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2025.101454.
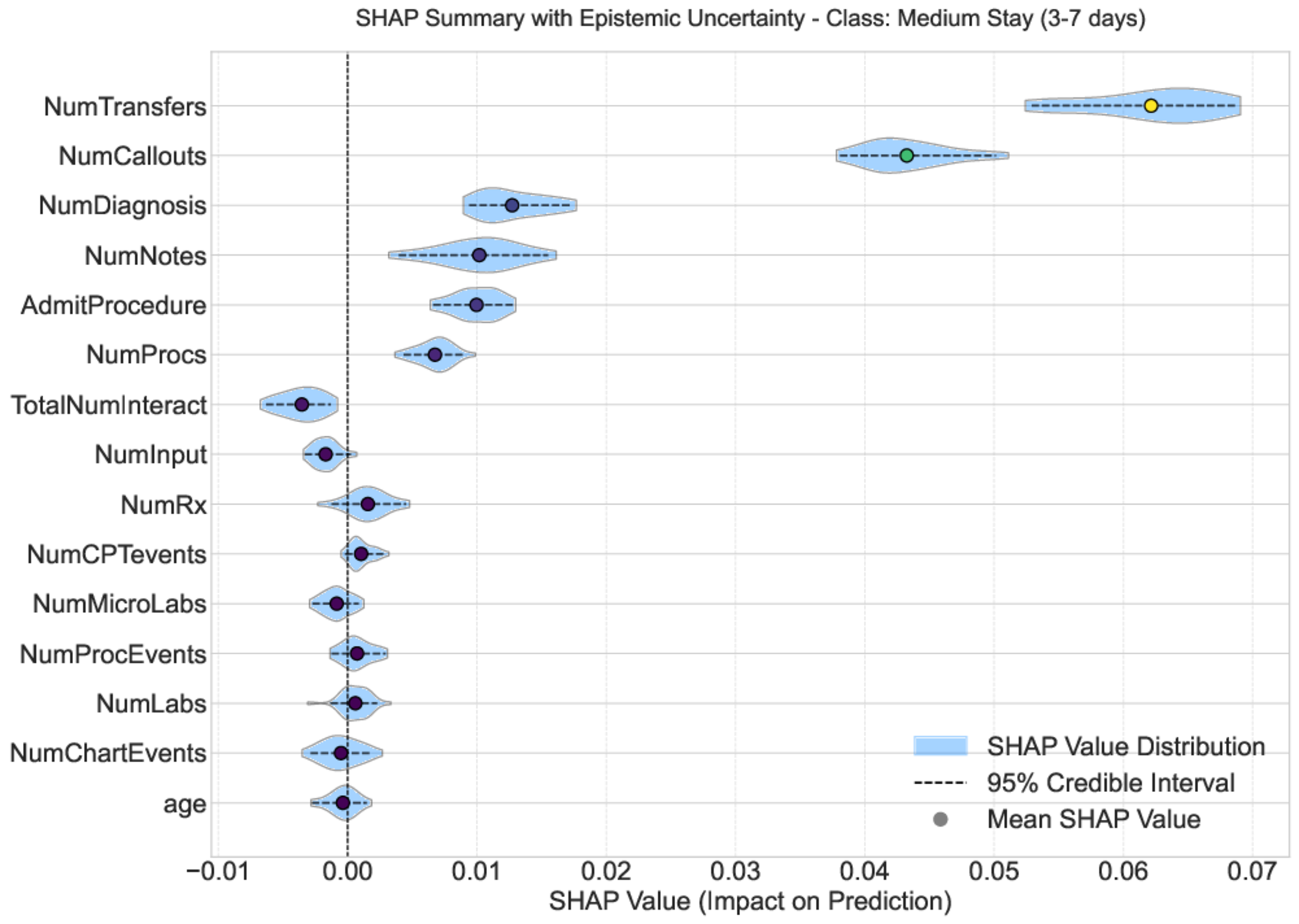
Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques, particularly Shapley additive explanations (SHAP), are essential for interpreting ensemble tree-based models in critical areas such as healthcare. However, SHAP values are often treated as point estimates that neglect uncertainty originating from aleatoric (irreducible noise) and epistemic (lack of data) sources. This work introduces an approach that decomposes SHAP value uncertainty into aleatoric, epistemic, and entanglement components. This approach employs Dempster-Shafer evidence theory and Dirichlet process (DP) hypothesis sampling over tree ensembles. The use-case validation reveals insights into epistemic uncertainty within SHAP explanations, enhancing the reliability and interpretability of SHAP attributions. This informs robust decision-making and model refinement. Our findings suggest that reducing epistemic uncertainty requires improved data quality and model development techniques. Tree-based models, particularly bagging, are effective in quantifying such uncertainties.